Feasibility of specimen self-collection in young children undergoing SARS-COV-2 surveillance for in person learning
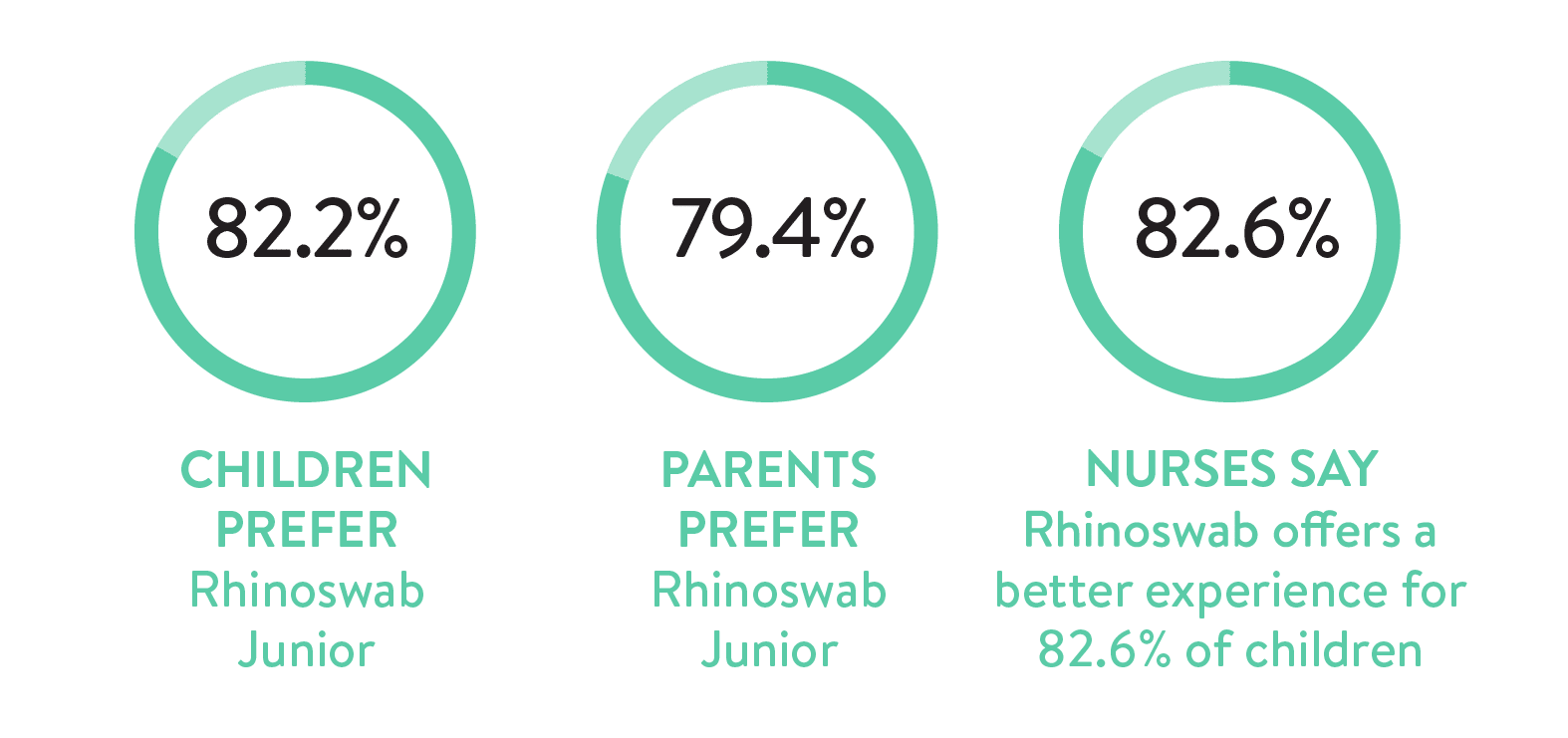
The study was conducted at a K-8 school in California with 296 participants to assess whether school children aged 5 to 14 years, can feasibly self-collect SARS-CoV-2 samples for surveillance testing over the course of an academic year. Clinical research staff provided all students with instructions to ensure proper technique. Errors occurred in 2.7% (n = … Read more